# React 源码解析(三)Fiber 的调度过程
本章进行 Fiber 的调度过程的分析,我们一起来看一下 react 是怎么调度任务的?
- Fiber 调度执行跟踪
- Fiber 调度原理分析
- Fiber 具体执行过程
# Fiber 调度执行跟踪
我们从上一章中的 scheduleWork 开始跟进。
- scheduleWork
- scheduleCallbackForRoot
- scheduleCallback
- Scheduler_scheduleCallback
- 调用 scheduler 库的 unstable_scheduleCallback 方法
方法 unstable_scheduleCallback 其实是在 scheduler 这个单独的库里。
import * as Scheduler from "scheduler";
const { unstable_scheduleCallback: Scheduler_scheduleCallback } = Scheduler;
2
提示
scheduler 源码版本为: 0.14.0
源码中可以看到,调度方法目前还是 unstable 版,后面肯定还会继续更新优化。
# Fiber 调度原理分析
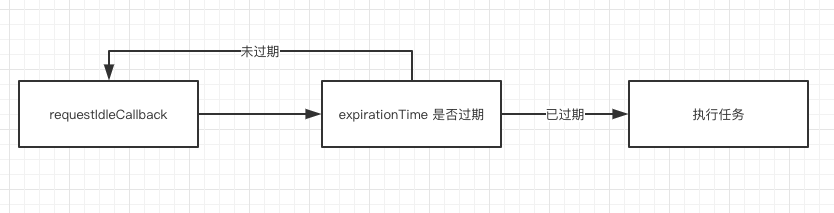
Fiber 调度原理的核心有两点:requestIdleCallback 方法 和 expirationTime 过期时间。
# 浏览器渲染频率
Fiber 的调度并不是凭空想象的,而是基于浏览器的渲染来设定的。
目前主流的屏幕刷新率都在 60hz,因此渲染一帧的时间为 1000 ms / 60 hz = 16.7ms。也就是说,每隔 16.7ms 就必须得刷新一下页面,不然用户就会感觉页面很卡顿,不流畅。
所以 react 在进行调度时,会优先保证 60hz 的浏览器渲染频率,如果有任务执行超过了 16.7ms,则可能会被 react 中断。
# requestIdleCallback 方法
requestIdleCallback 定义如下:window.requestIdleCallback 会在浏览器空闲时期依次调用函数,这就可以让开发者在主事件循环中执行后台或低优先级的任务。函数一般会按先进先调用的顺序执行,然而,如果回调函数指定了执行超时时间 timeout,则有可能为了在超时前执行函数而打乱执行顺序。
通俗一点的理解来说,requestidleCallback 会在主线程空闲的时候进行调用,这样在代码执行时,就不会影响页面的刷新渲染,用户就不会感到卡顿。
requestIdleCallback 的兼容性
当前 requestIdleCallback 的兼容性并不是特别好,所以 react 并没有直接使用 requestIdleCallback 进行任务的调度,而是通过 requestAnimationFrame 去模拟了 requestIdleCallback 的功能。
# requestAnimationFrame 方法
requestAnimationFrame 定义如下:window.requestAnimationFrame 告诉浏览器你希望执行一个动画,并且要求浏览器在下次重绘之前调用指定的回调函数更新动画。该方法需要传入一个回调函数作为参数,该回调函数会在浏览器下一次重绘之前执行。
当你准备更新动画时你应该调用此方法。这将使浏览器在下一次重绘之前调用你传入给该方法的回调函数。回调函数执行次数通常是每秒 60 次,因为在大多数遵循 W3C 建议的浏览器中,回调函数执行次数通常与浏览器屏幕刷新次数相匹配,即 16.7ms 执行一次。
function logLoop() {
var now = new Date();
while (true) {
var newNow = new Date();
if (newNow - now > 20) {
break;
}
}
console.log(performance.now());
requestAnimationFrame(logLoop);
}
logLoop();
// 7300.494999999501
// 7316.084999998566
// 7333.24999999968
// 7351.334999999381
// 7367.234999997891
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
可以看到,在循环调用 requestAnimationFrame 时,平均会在 16.7ms 进行一次调用。
# Fiber 具体执行过程
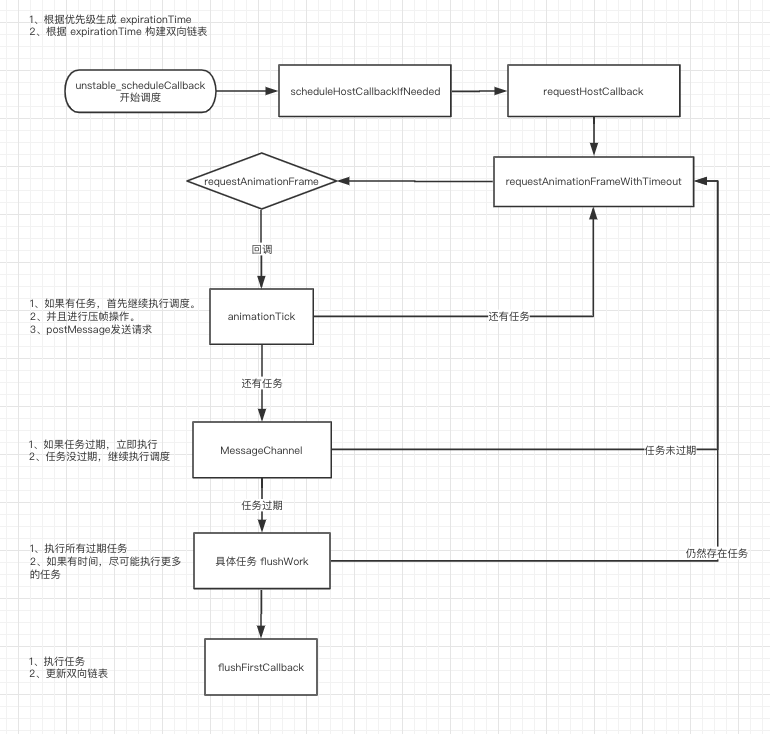
Fiber 具体执行过程如下:
- 获取当前系统的开始时间。
- 根据任务优先级别设置对应的过期时间。
- 根据过期时间进行双向链表的排序。
- 排完序后调用 scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded 执行任务。
- 调用 requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout 在每一帧之后的空闲时间开始执行任务。
- requestAnimationFrame 回调时执行 animationTick 方法,计算帧过期时间并压缩帧。
- animationTick 执行完成后,调用 port.postMessage 传递消息。
- MessageChannel 接收到 postMessage 消息,开始具体执行任务。
- 执行 flushWork(prevScheduledCallback)最终执行调度。
- 调用 flushFirstCallback 最后执行任务,并更新双向链表。
调度原则:
- 有过期的任务先全部执行完,没过期任务尽可能多的执行。
- 没执行完的任务继续调用 scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded 进行调度。
接下来,我们从源码部分一步一步跟进。
# 源码解析
# 获取当前系统时间
获取系统时间,默认使用 performance.now 方法,表示页面渲染成功后到目前的时间段,如果此方法不支持,则降级使用 Date.now 方法。
function unstable_scheduleCallback(
priorityLevel,
callback,
deprecated_options
) {
var startTime =
currentEventStartTime !== -1
? currentEventStartTime
: exports.unstable_now();
}
// unstable_now 方法如下
var localDate = Date;
if (hasNativePerformanceNow) {
var Performance = performance;
exports.unstable_now = function() {
return Performance.now();
};
} else {
exports.unstable_now = function() {
return localDate.now();
};
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 根据任务优先级设置 expirationTime
Scheduler 是根据 expirationTime 来表示任务优先级的,优先级越高 expirationTime 越小,表示需要尽快执行。
var maxSigned31BitInt = 1073741823;
// 立马过期,ImmediatePriority
var IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = -1;
// 250ms 以后过期
var USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY = 250;
var NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 5000;
var LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 10000;
// 永不过期
var IDLE_PRIORITY = maxSigned31BitInt;
switch (currentPriorityLevel) {
case ImmediatePriority:
expirationTime = startTime + IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case UserBlockingPriority:
expirationTime = startTime + USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY;
break;
case IdlePriority:
expirationTime = startTime + IDLE_PRIORITY;
break;
case LowPriority:
expirationTime = startTime + LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case NormalPriority:
default:
expirationTime = startTime + NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
从源码中可以看到,立即执行的优先级 Timeout = -1,表示任务已过期,需要立即执行。
# 根据过期时间进行双向链表的排序
Scheduler 在进行任务调度时,可能同时有很多任务被加入进来,scheduler 会根据任务的优先级进行排序,最终构建一个双向链表的数据结构。
var newNode = {
callback: callback, // 任务具体的内容
priorityLevel: currentPriorityLevel, // 任务优先级
expirationTime: expirationTime, // 任务的过期时间
next: null, // 下一个节点
previous: null // 上一个节点
};
// 插入指定节点
// Insert the new callback into the list, ordered first by expiration, then
// by insertion. So the new callback is inserted any other callback with
// equal expiration.
if (firstCallbackNode === null) {
// This is the first callback in the list.
firstCallbackNode = newNode.next = newNode.previous = newNode;
// 排完顺序之后按照指定的规则执行任务。
// 什么时候执行呢?在每一帧绘制完成之后的空闲时间。
scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded();
} else {
var next = null;
var node = firstCallbackNode;
do {
if (node.expirationTime > expirationTime) {
// The new callback expires before this one.
next = node;
break;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node !== firstCallbackNode);
if (next === null) {
// No callback with a later expiration was found, which means the new
// callback has the latest expiration in the list.
next = firstCallbackNode;
} else if (next === firstCallbackNode) {
// The new callback has the earliest expiration in the entire list.
firstCallbackNode = newNode;
scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded();
}
var previous = next.previous;
previous.next = next.previous = newNode;
newNode.next = next;
newNode.previous = previous;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 调用 scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded
排完序后调用 scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded 执行任务。
function scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded() {
if (firstCallbackNode !== null) {
// 根据列表中最早的过期时间进行调度。
// Schedule the host callback using the earliest expiration in the list.
var expirationTime = firstCallbackNode.expirationTime;
if (isHostCallbackScheduled) {
// Cancel the existing host callback.
cancelHostCallback();
} else {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
}
requestHostCallback(flushWork, expirationTime);
}
}
requestHostCallback = function(callback, absoluteTimeout) {
scheduledHostCallback = callback;
timeoutTime = absoluteTimeout;
if (isFlushingHostCallback || absoluteTimeout < 0) {
// Don't wait for the next frame. Continue working ASAP, in a new event.
// 如果过期了,别等了,尽快执行。
port.postMessage(undefined);
} else if (!isAnimationFrameScheduled) {
// If rAF didn't already schedule one, we need to schedule a frame.
// TODO: If this rAF doesn't materialize because the browser throttles, we
// might want to still have setTimeout trigger rIC as a backup to ensure
// that we keep performing work.
isAnimationFrameScheduled = true;
// 这个函数就是根据每一帧的空闲时间来进行更新的。
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick);
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 调用 requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout
调用 requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout 在每一帧之后的空闲时间开始执行任务。
var ANIMATION_FRAME_TIMEOUT = 100;
var rAFID = void 0;
var rAFTimeoutID = void 0;
var requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout = function(callback) {
// 循环调用 requestAnimationFrame,因为 callback 中会继续调用 requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout
rAFID = localRequestAnimationFrame(function(timestamp) {
// cancel the setTimeout
localClearTimeout(rAFTimeoutID);
callback(timestamp);
});
// 判断浏览器 tab 页切换用。
rAFTimeoutID = localSetTimeout(function() {
// cancel the requestAnimationFrame
localCancelAnimationFrame(rAFID);
callback(exports.unstable_now());
}, ANIMATION_FRAME_TIMEOUT);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 调用 animationTick
requestAnimationFrame 回调时执行 animationTick 方法,计算帧过期时间并压缩帧。
var frameDeadline = 0;
// 我们开始假设我们以 30fps 的速度运行,但是如果我们得到更频繁的动画帧,会进行动态调整,将这个值调整为更快的 fps。
var previousFrameTime = 33;
var activeFrameTime = 33;
// animationTick 方法,计算帧过期时间并压缩帧。
var animationTick = function(rafTime) {
if (scheduledHostCallback !== null) {
// 有任务再进行递归,没任务的话不需要工作。
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick);
} else {
// No pending work. Exit.
isAnimationFrameScheduled = false;
return;
}
// rafTime 是 requestAnimationFrame 回调函数中返回的参数,参数值与 performance.now 的返回值相同。
// activeFrameTime 默认 33
var nextFrameTime = rafTime - frameDeadline + activeFrameTime;
// 连续比较 2 次 FrameTime,可以得出是否需要对帧率进行调整。
if (nextFrameTime < activeFrameTime && previousFrameTime < activeFrameTime) {
// 不兼容 120hz 的渲染频率,可能是个 bug
if (nextFrameTime < 8) {
nextFrameTime = 8;
}
// 如果一个帧变长,那么下一个帧可能会变短以赶上。
// 如果两个帧都连续短,那么这表明我们实际上具有比我们当前的帧速率更高的帧速率。
// 我们相应地动态调整帧率。例如,如果我们在 120h z显示器或 90hz VR 显示器上运行。取两个中的最大值,以防其中一个由于错过帧截止日期而异常。
activeFrameTime =
nextFrameTime < previousFrameTime ? previousFrameTime : nextFrameTime;
} else {
previousFrameTime = nextFrameTime;
}
// 计算当前帧的截止时间,用开始时间加上当前帧渲染时间
frameDeadline = rafTime + activeFrameTime;
if (!isMessageEventScheduled) {
isMessageEventScheduled = true;
// 通知 MessageChannel 发送数据
port.postMessage(undefined);
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# MessageChannel 负责具体的调度
MessageChannel 接收到 postMessage 消息,开始具体执行任务。
// 1、使用 postMessage 巧妙地将空闲工作推迟到重新绘制之后。
// 2、在每一帧开始的rAF的回调里记录每一帧的开始时间,并计算每一帧的过期时间。
// 3、通过 messageChannel 发送消息。在帧末 messageChannel 的回调里接收消息,
// 4、根据当前帧的过期时间和当前时间进行比对来决定当前帧能否执行任务。
// 5、如果能的话会依次从任务链表里拿出队首任务来执行。
// 6、执行尽可能多的任务后如果还有任务,下一帧再重新调度。
var channel = new MessageChannel();
var port = channel.port2;
// 下面的代码逻辑决定当前帧要不要执行任务。
// 1、如果当前帧没过期,说明当前帧有富余时间,可以执行任务。
// 2、如果当前帧过期了,说明当前帧没有时间了,这里再看一下当前任务 firstCallbackNode 是否过期
// 如果过期了也要执行任务;如果当前任务没过期,说明不着急,那就先不执行。
channel.port1.onmessage = function(event) {
isMessageEventScheduled = false;
var prevScheduledCallback = scheduledHostCallback;
var prevTimeoutTime = timeoutTime;
scheduledHostCallback = null;
timeoutTime = -1;
var currentTime = exports.unstable_now();
var didTimeout = false;
if (frameDeadline - currentTime <= 0) {
if (prevTimeoutTime !== -1 && prevTimeoutTime <= currentTime) {
// 任务过期
didTimeout = true;
} else {
// 未超时
if (!isAnimationFrameScheduled) {
isAnimationFrameScheduled = true;
// 当前帧由于浏览器渲染等原因过期了,那就去下一帧再处理。
requestAnimationFrameWithTimeout(animationTick);
}
// Exit without invoking the callback.
scheduledHostCallback = prevScheduledCallback;
timeoutTime = prevTimeoutTime;
return;
}
}
if (prevScheduledCallback !== null) {
isFlushingHostCallback = true;
try {
// 最终执行
prevScheduledCallback(didTimeout);
} finally {
isFlushingHostCallback = false;
}
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
# flushwork 具体执行任务
由上文可以看到最终调用的方法是 prevScheduledCallback,经过跟踪,该方法其实是 flushWork。
function flushWork(didUserCallbackTimeout) {
// 如果当前处于暂停状态,则马上退出。
if (enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused) {
return;
}
// 在调度下一次工作时,我们需要一个新的 host callback。
isHostCallbackScheduled = false;
isPerformingWork = true;
var previousDidTimeout = currentHostCallbackDidTimeout;
currentHostCallbackDidTimeout = didUserCallbackTimeout;
try {
// 如果是任务过期了,赶紧排队把过期的任务给执行了
if (didUserCallbackTimeout) {
while (
firstCallbackNode !== null &&
!(enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused)
) {
// TODO Wrap in feature flag
// Read the current time. Flush all the callbacks that expire at or
// earlier than that time. Then read the current time again and repeat.
// This optimizes for as few performance.now calls as possible.
var currentTime = exports.unstable_now();
if (firstCallbackNode.expirationTime <= currentTime) {
do {
flushFirstCallback();
} while (
firstCallbackNode !== null &&
firstCallbackNode.expirationTime <= currentTime &&
!(enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused)
);
continue;
}
break;
}
} else {
// 当前帧有富余时间,while 的逻辑是只要有任务且当前帧没过期就去执行任务。
// 执行队首任务,把队首任务从链表移除,并把第二个任务置为队首任务。
// 执行任务可能产生新的任务,再把新任务插入到任务链表
if (firstCallbackNode !== null) {
do {
if (enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused) {
break;
}
flushFirstCallback();
// shouldYieldToHost 代表当前帧过期了,取反的话就是没过期。
} while (firstCallbackNode !== null && !shouldYieldToHost());
}
}
} finally {
isPerformingWork = false;
currentHostCallbackDidTimeout = previousDidTimeout;
// 如果仍然存在剩余工作,则继续执行
scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded();
}
}
shouldYieldToHost = function() {
return frameDeadline <= exports.unstable_now();
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# flushFirstCallback 具体执行任务,更新当前的双向链表
接下来走到 flushFirstCallback 方法,具体执行任务,更新当前的双向链表。
function flushFirstCallback() {
var currentlyFlushingCallback = firstCallbackNode;
// 在调用回调之前从列表中删除节点。这样即使回调抛出异常,列表也处于一致状态。
var next = firstCallbackNode.next;
if (firstCallbackNode === next) {
// 这是列表中的最后一个回调。
firstCallbackNode = null;
next = null;
} else {
var lastCallbackNode = firstCallbackNode.previous;
firstCallbackNode = lastCallbackNode.next = next;
next.previous = lastCallbackNode;
}
currentlyFlushingCallback.next = currentlyFlushingCallback.previous = null;
// 现在可以安全地调用 callback 了。
var callback = currentlyFlushingCallback.callback;
var expirationTime = currentlyFlushingCallback.expirationTime;
var priorityLevel = currentlyFlushingCallback.priorityLevel;
var previousPriorityLevel = currentPriorityLevel;
var previousExpirationTime = currentExpirationTime;
currentPriorityLevel = priorityLevel;
currentExpirationTime = expirationTime;
var continuationCallback;
try {
var didUserCallbackTimeout =
currentHostCallbackDidTimeout ||
// Immediate 优先级 callback 总是像超时一样调用。
priorityLevel === ImmediatePriority;
// 🍎 这里才是最终执行任务
continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout);
} catch (error) {
throw error;
} finally {
currentPriorityLevel = previousPriorityLevel;
currentExpirationTime = previousExpirationTime;
}
// A callback may return a continuation. The continuation should be scheduled
// with the same priority and expiration as the just-finished callback.
// 如果 callback 返回了一个继续调度的任务。应以同样的优先级调度此任务。
if (typeof continuationCallback === "function") {
// 以下内容和初始化构建双向链表的代码几乎一致。
var continuationNode = {
callback: continuationCallback,
priorityLevel: priorityLevel,
expirationTime: expirationTime,
next: null,
previous: null
};
// Insert the new callback into the list, sorted by its expiration. This is
// almost the same as the code in `scheduleCallback`, except the callback
// is inserted into the list *before* callbacks of equal expiration instead
// of after.
// 将新回调插入到列表中,并按其过期时间排序。这是几乎与 schedulecallback 中的代码相同,只是回调被插入到列表之前的回调中,而不是之后的回调。
if (firstCallbackNode === null) {
// 这是列表中的第一个回调。
firstCallbackNode = continuationNode.next = continuationNode.previous = continuationNode;
} else {
var nextAfterContinuation = null;
var node = firstCallbackNode;
do {
if (node.expirationTime >= expirationTime) {
// This callback expires at or after the continuation. We will insert
// the continuation *before* this callback.
// 此回调在 continuation 时或之后到期。 我们将在此回调之前插入 continuation。
nextAfterContinuation = node;
break;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node !== firstCallbackNode);
if (nextAfterContinuation === null) {
// 找不到相同或优先级更低的回调,这意味着 callback 是列表中优先级最低优先级的回调。
nextAfterContinuation = firstCallbackNode;
} else if (nextAfterContinuation === firstCallbackNode) {
// 新回调是列表中优先级最高的回调。
firstCallbackNode = continuationNode;
scheduleHostCallbackIfNeeded();
}
var previous = nextAfterContinuation.previous;
previous.next = nextAfterContinuation.previous = continuationNode;
continuationNode.next = nextAfterContinuation;
continuationNode.previous = previous;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
# 总结
这一章分析了 fiber 具体的调度过程,用一张图来总结一下吧。